Digital Manufacturing - Resource Orchestration
Resource Orchestration
SAP Digital Manufacturing’s Resource Orchestration module is a powerful tool designed to optimize the allocation and use of resources on the manufacturing floor.
Optimally execute your digital operations.
- Adaption to short-term or ad hoc changes on the shop floor. Heuristics to support active backlog orders and automatically propose scheduled plans based on shop floor situation
- Manage Labor and tools planning on the shop floor
- Visualize planned downtimes of machines and quickly respond to unplanned downtimes via rescheduling options
- Monitor production progress and adapt to any changes in the execution of shop floor activities
- Create labor shift plans and publish them to operators
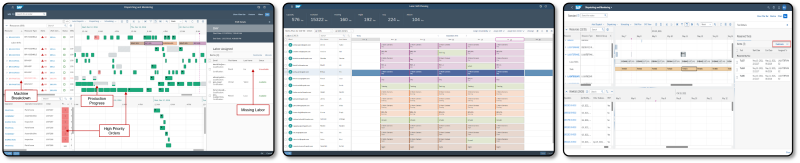
Orchestrate and control the shop floor
- Monitor the entire manufacturing process to optimize resources and execution
- Role-specific Fiori and operator dashboards
- Fully configurable Production Operator Dashboard (POD) that supports drag & drop and preview
- Monitor OEE and manage downtime events
- Resource Orchestration to manage shop floor workflow and labor assignments
- Automation interfaces to provide for shop- floor-driven manufacturing events and data collection
Resource Orchestration & Dispatching
- Orchestrate labor and resources on the shop floor to achieve maximum availability
- React quickly to unexpected events utilizing built-in intelligence
- Dispatch and sequence operations to reflect the “real world” on the shop floor
- Provides multiple options for dispatching: Operations can be dispatched on the Resource level (e.g., for Job Shop scenarios), or Operations can be dispatched on the Work Center level (e.g., for Production lines or Production cells)
- Monitor the entire manufacturing process to optimize resources and execution
- reflect the reality on the shop floor by visualizing high-priority orders, machine breakdowns, missing labor, and production progress
- Automatically dispatch operations from the Work List
- Trigger order release from order view and Gantt Chart and show created SFCs
- Operations can be split, merged, and distributed to alternative resources
- Split quantities are shown in the order schedule information of the POD
- Tight POD integration to reflect planning situation on the shop floor and to visualize changes from execution in planning and vice versa
- Automatically or manually dispatch operations using the Work Center view
- Check and reserve tools from the planning board
- Automatically schedule the backlog orders with advanced heuristics
Resource Orchestration- Labor Scheduling
- Manage shifts and labor considering labor qualification and certification
- Assign labor to work centers and, if required, to time intervals
- In the situation where workers are not available, the unavailability of the worker(s) can be entered for the corresponding day or week
- Unavailability can also be entered in time slices if the unavailability is only for a few hours
- Assignments are considered during dispatching in the Gantt Chart of the scheduling and dispatching app
- KPIs visualize the status for the selected week: Capacity reflects available labor capacity, and Demand reflects demand coming from the orders
- Send emails to operators using the Schedule Labor app
Automation: IT/OT Convergence
IT/OT convergence in digital manufacturing refers to integrating Information Technology (IT) systems, which handle data and communication, with Operational Technology (OT) systems, which manage industrial operations and physical equipment. The need for real-time data analysis, predictive maintenance, and automated decision-making in the manufacturing process drives this convergence.
In digital manufacturing, IT/OT convergence allows for seamless communication between the factory floor and the enterprise level, resulting in improved efficiency, productivity, and flexibility. It enables data collected from OT systems, such as sensors and machines, to be processed and analyzed by IT systems, providing actionable insights for operational improvements, energy management, and supply chain optimization.
This integration also supports advanced manufacturing technologies like the Internet of Things (IoT), Artificial Intelligence (AI), and robotics, which are central to the concept of Industry 4.0. By bridging the gap between IT and OT, manufacturers can leverage the full potential of digital transformation, leading to smarter, more autonomous, and connected manufacturing environments.
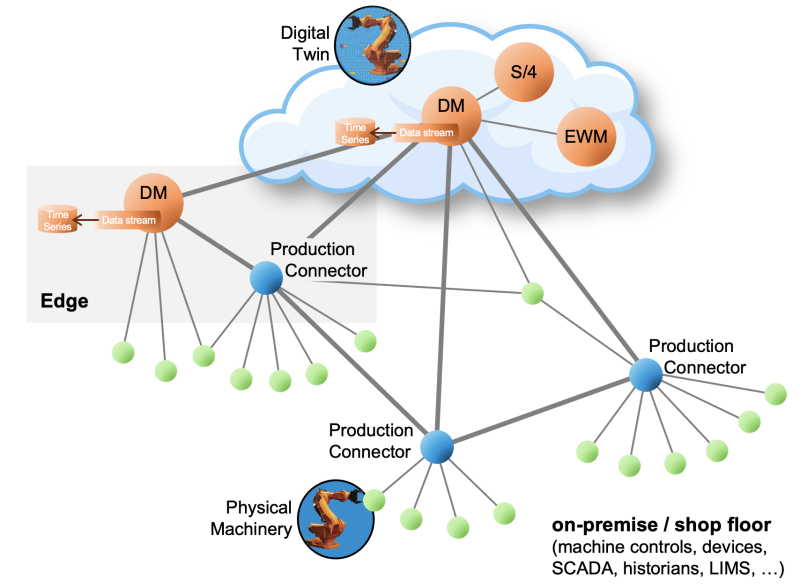
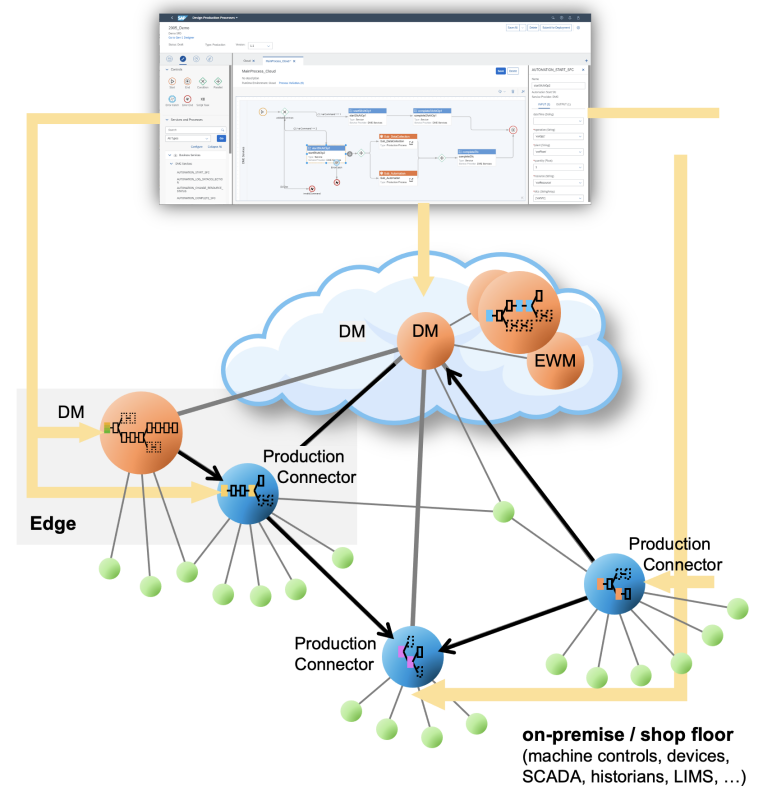
Model the network of all production-relevant systems in your landscape
- From IT systems to OT systems
- From the top floor to the shop floor
- From cloud to edge and on-premise
Model “Digital Twins” in the cloud (IT) for a vertical connection with local on-premise systems and the physical machinery on the shop floor (OT). Let “Production Connectivity” do all data exchange between IT and OT to read data from shop floor systems for data collection or decision-making (DM Execution). Push data actively to Cloud or Edge to analyze, give insights, and write data (set points) to shop floor systems for production control, and observe measurements on the shop floor to take action if a condition on them is fulfilled (e.g. if a measurement raises a threshold).
IT/OT Convergence to Run Production from end-2-end
Designing production processes: Orchestrating service calls from the own system and connected systems. These processes can be executed on different runtimes in SAP Digital Manufacturing Cloud, SAP DM Edge, or next to the machines on the SAP Production Connector.
Integrate vertically: Converge IT services from top-floor systems with OT services from shop-floor systems.
Integrate horizontally: Realizing the entire production process from the raw material to its finished good. Processes can call each other on the same or connected runtimes.
Deploy processes: from the DM design time in the cloud (Production Process Designer, PPD) to their related runtimes for which they are designed (SAP DM cloud, SAP DM edge, or SAP Production Connector).
Start deployed processes
- either automatically, by a scheduler, with events on the top floor (e.g., “shop order created”) or when conditions on shop floor system tags become true (e.g., “temperature>500”),
- or manually, that is, by the operator pressing a button on the production operator dashboard (POD) or the supervisor handling an alert in the alert inbox (alert management).
Monitor: Process execution and debug it to find errors.
Optimize Production by feeding back any findings from the operation into the process designs.
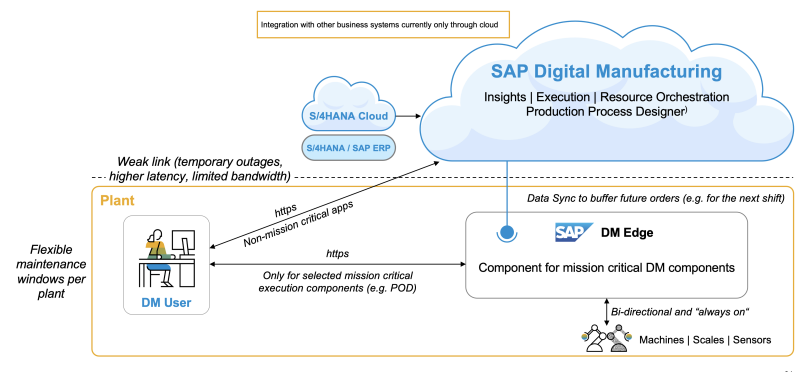
Edge Computing
Manufacturing Edge Computing describes the capability of connecting, processing, storing, and analyzing machine data, thereby supporting production processes (incl. user interaction) closer to the data source and on the shop floor to enable faster decision-making and to operate with intermittent connectivity to the cloud.
SAP Digital Manufacturing for edge computing provides maximum business continuity for mission-critical applications in manufacturing.